Computer simulation is a capable strategy for outline and examination and complex frameworks. The general approach in a computer simulation is to speak to the dynamic qualities of a true framework in a PC show. The model is subjected to analyses to get prescient data helpful in settling on educated basic leadership about the attributes of the genuine framework.
Simulations are appropriate for issues in which there are no which there are no closed-form analytical solutions. Since most unique issues practically speaking cannot be represented and solved completely utilizing scientific conditions, PC reproduction is an intense and adaptable approach in complex frameworks investigation.
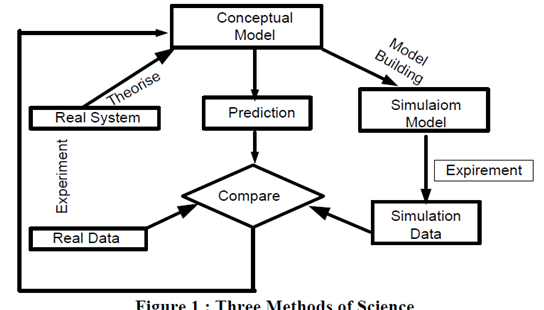
Simulations can be classified into
- continuous simulation
- discrete simulations.
What Do You Mean By Discrete Simulation Language?Explain Its Classifications
In continuous Simulations, the state factors, i.e., the accumulation of factors expected to depict the framework, change persistently after some time and the conduct of the framework is normally portrayed by differential conditions. Cases of constant frameworks incorporate the demonstrating of warm or pressure driven frameworks.
Discrete Simulations are occasion driven where the state factors change at discrete time focuses. Cases of discrete simulation incorporate administration industry applications, for example, lines in a supermarket and assembling applications including material stream examination.
What is a computer simulation? Definition of online digital technology.Difficulties occur in computer simulation and its advantages.
Briefly, we can state that Simulation is
- Simulated framework emulates operation of genuine framework after some time
- Artificial history of framework can be created and watched
- Internal (maybe inconspicuous) conduct of framework can be studied
- Timescale can be modified as required
- Conclusions about real framework qualities can be derived real framework is contrasted and Simulations
Explain software maintenance ? explain its various types of models ?
Formal Definition
Simulations can be comprehensively characterized as a method for concentrate genuine dynamical frameworks by impersonating their conduct utilizing a numerical model of the system implemented on a computerized PC.
What is a computer simulation? Definition of online digital technology.Difficulties occur in computer simulation and its advantages.
Simulations can likewise be seen as a numerical method for settling muddled likelihood models, normal differential condition and fractional differential condition, similarly to the route in which we can utilize a PC to numerically assess the basic of a confused capacity. That is the reason investigation of reproduction is considered as an interdisciplinary subject.
What is a computer simulation? Definition of online digital technology.Difficulties occur in computer simulation and its advantages.
Application Areas of Simulation
- Manufacturing
- Computer Systems
- E-business/work process frameworks
- Finance
- Telecommunications
- Transportation
- Military
Advantages
- Simulation discretionary model multifaceted nature
- Circumvents systematically intractable models
- Facilitates imagine a scenario where and affectability investigations.
- Building a model can prompt framework changes
- Greater comprehension can be utilized to confirm logical arrangements
Disadvantages
Simulations give just gauges of arrangement, just tackles one parameter at any given moment, can take a lot of advancement as well as PC time. Try not to utilize PC Simulations if a sound judgment or diagnostic arrangement is accessible, or if assets are deficient, or if recreation costs exceed benefits.
Difficulties of Simulation
- Provides just individual, not general arrangements
- Manpower and tedious
- Computing memory and time-escalated
- Difficult so specialists are required
- Hard to translate comes about
- Expensive
At the point when to Use Simulation?
- Study internals of a mind boggling framework e.g. organic framework
- Optimize a current outline e.g. directing calculations, sequential construction system
- Examine impact of natural changes e.g. climate guaging
- System is hazardous or ruinous e.g. nuclear bomb, nuclear reactor, rocket propelling
- Study significance of factors
- Verify diagnostic arrangements (hypotheses)
- Test new plans or arrangements
- Impossible to watch/impact/manufacture the framework
- When it permits examination of framework internals that may not generally be discernible
- Observation of the reenactment gives bits of knowledge into framework conduct
- System parameters can be balanced in the simulation demonstrate permitting appraisal of their affectability (size of effect on general framework conduct)
- Simulation confirms examination of a mind boggling framework, or can be utilized as an instructing apparatus to give knowledge into scientific systems
- A test system can be utilized for guideline, abstaining from tying up or harming a costly, genuine framework (e.g., a flight recreation versus utilization of multimillion dollar air ship)